Iron-air batteries are an emerging technology that could revolutionize grid-scale energy storage. By harnessing the power of reversible rusting, these innovative batteries offer a cost-effective and environmentally friendly solution for storing large amounts of energy over extended periods. With the potential to significantly reduce costs compared to lithium-ion batteries and provide long-duration storage, iron-air batteries are attracting increasing attention as a key enabler for the integration of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power into the electrical grid.
Iron-Air Battery Components
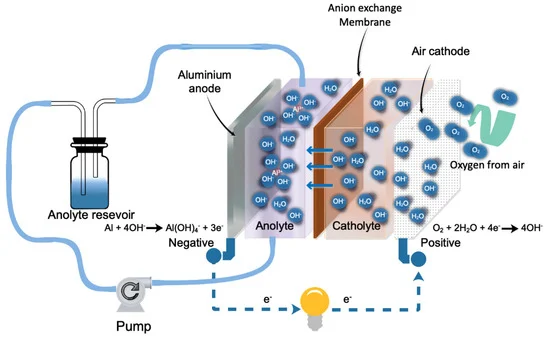
Iron-air batteries consist of three main components: an iron anode that undergoes oxidation during discharge, a porous cathode that allows oxygen from the air to enter and react with the electrolyte, and a water-based electrolyte solution that conducts ions between the anode and cathode. The unique design and materials used in these batteries contribute to their high energy density, cost-effectiveness, and environmental benefits compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
Advantages and Challenges
Iron-air batteries offer several advantages, including high energy density, making them suitable for long-duration energy storage, and cost-effectiveness due to the abundance and low cost of iron compared to lithium-ion batteries. They also have a lower environmental impact, as they use non-toxic materials.
However, iron-air batteries face challenges related to efficiency, as they experience energy losses during the oxidation and reduction processes. They are also larger and heavier than other battery types, limiting their use in portable applications. Additionally, their slower charge and discharge rates may restrict their use in applications requiring rapid energy delivery.
Grid-Scale Energy Storage
Iron-air batteries are particularly promising for grid-scale energy storage applications, where they can store large amounts of energy for extended periods. By providing reliable and long-term storage solutions, these batteries can help balance the variability of renewable energy sources like wind and solar power, enabling their integration into the electrical grid. The low cost and high energy density of iron-air batteries make them an attractive option for utilities seeking to decarbonize their power generation while maintaining grid stability and reliability.






